New Delhi: A new study on Monday showed novel insights into how pathogens invade the lungs using lab-grown lung microtissues generated from human stem cells.
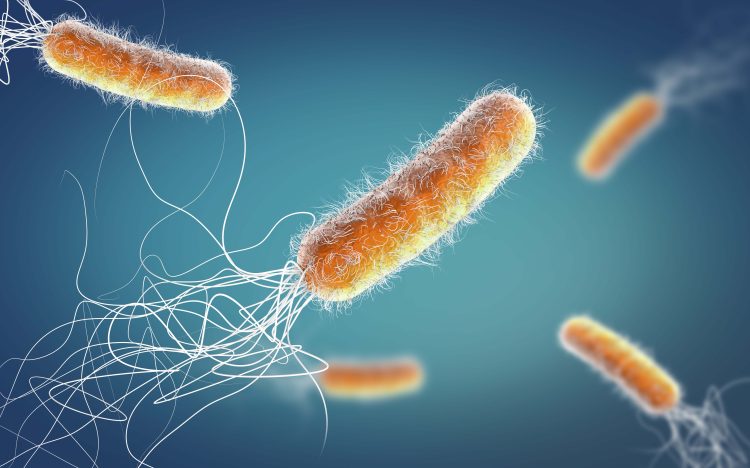
The team from the Biozentrum of the University of Basel in Switzerland focussed on Pseudomonas aeruginosa, part of WHO’s list of 12 of the world’s most dangerous bacterial pathogens.
The bacterium targets specific lung cells and has developed a sophisticated strategy to break through the lungs’ line of defence. It is especially threatening to immunocompromised patients and those on mechanical ventilation, with mortality rates up to 50 per cent.
In the journal Nature Microbiology, the team describes how Pseudomonas breaches the top layer of lung tissue and invades deeper areas by using lab-grown human lung microtissues that realistically mimic the infection process inside a patient’s body. “These lung models enabled us to uncover the pathogen’s infection strategy. It uses the mucus-producing goblet cells as Trojan horses to invade and cross the barrier tissue. By targeting the goblet cells, which make up only a small part of the lung mucosa, the bacteria can breach the defence line and open the gate,” said Prof Urs Jenal at the Biozentrum.
Pseudomonas attacks and invades the goblet cells via secretion systems. It then replicates inside the cells and ultimately kills them. The burst of the dead cells leads to ruptures in the tissue layer, affecting the protective barrier. With this, the pathogens rapidly colonise and spread into deeper tissue regions.
Jenal’s team also developed a biosensor to measure and track a small signalling molecule called c-di-GMP in individual bacteria in real-time.
(IANS)