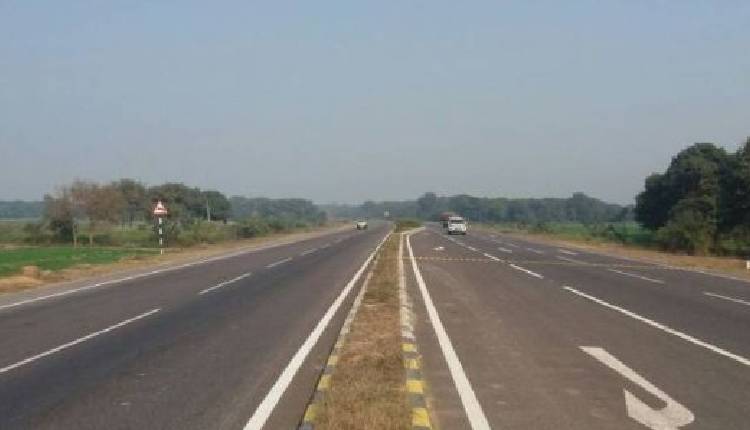
New Delhi: The length of India’s National Highway network has surged by 60 per cent in the last 10 years from 91,287 km in 2014 to 146,195 km in 2024, making it the second largest road network in the world, according to the year-end review of the Ministry of Road Transport and Highways released on Thursday.
In a landmark achievement, National High-Speed Corridors have also increased from a mere 93 km in 2014 to 2,474 km in 2024 which reflects the quantum improvement in the country’s infrastructure.
The rapid growth in the country’s highways has taken place due to the Centre’s policies including flagship programmes such as the Bharatmala Pariyojana, the official statement said.
Another 2,540 km of highways have been added through externally Aided Projects (EAP) with loan assistance from the World Bank, the Japan International Cooperation Agency (JICA), and the Asian Development Bank (ADB) as on November 30, 2024, according to the statement.
The Cabinet Committee on Economic Affairs, chaired by Prime Minister Narendra Modi, also approved the development of 8 important National High-Speed Corridor projects with a length of 936 km at a cost of Rs 50,655 crore across the country. Implementation of these projects will generate an estimated 4.42 crore man-days of direct and indirect employment.
Under Asset Monetisation following the TOT (Toll Operate and Transfer) model, NHAI monetised four TOT bundles realising Rs 15,968 crore during FY 2023-24, totalling Rs 42,334 crore so far. During the FY 2024-25, NHAI has awarded TOT Bundle 16 of a 251 km-long stretch on the Hyderabad-Nagpur corridor of NH-44 in Telangana to M/s Highway Infrastructure Trust for Rs 6,661 crores for 20 years.
The Ministry of Road Transport and Highways (MoRTH) plans to develop a network of 35 Multimodal Logistics Parks as part of Bharatmala Pariyojana with a total investment of about Rs 46,000 crore, which once operational, will be able to handle around 700 million metric tonnes of cargo. Of this, MMLPs at 15 prioritised locations will be developed with a total investment of about Rs. 22,000 crore.
These MMLPs will serve as regional cargo aggregation and distribution hubs for various industrial and agricultural nodes, consumer hubs and EXIM gateways such as seaports with multi-modal connectivity. In certain cases, the MMLPs are also being developed in tandem with the Inland Waterway Terminals under the Sagarmala Pariyojana to further reduce the cost of inland cargo movement at a much larger scale as compared to conventional road-based movement, the statement further explained.
To ensure adequate last-mile connectivity to all operational ports in the country, the MoRTH has developed a comprehensive Port Connectivity Masterplan for the Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade identifying connectivity requirements for which 59 critical infrastructure projects of length of about 1,300 km have been selected for implementation, the statement explained.
The Prime Minister has dedicated multiple road development projects to the nation improving connectivity and helping in economic development in that region. Among the major projects inaugurated this year was the 2,320-metre-long cable-stayed Sudarshan Setu Bridge (Okha-Beyt Dwarka Signature bridge), built at a cost of around Rs 980 crore connecting Okha mainland and Beyt Dwarka island. The iconic bridge will also serve as a major tourist attraction of Devbhumi Dwarka.
Other projects include the All India Tourist Permit Module developed by NIC allows tourist vehicle operators to transport tourists and their luggage across India, simplifying interstate travel, enhancing mobility and supporting the tourism sector by eliminating the need for multiple permits.
The government is also formulating a scheme to provide cashless treatment to victims of road accidents caused by the use of motor vehicles.
Besides, the government introduced the Registered Vehicle Scrapping Facilities which are now operational across 19 states and UTs and 66 additional centres are under construction.
High priority has also been accorded to the identification and rectification of blackspots (accident-prone spots) on National Highways, making concerted efforts towards improvement of road safety through engineering measures, the review added.
(IANS)