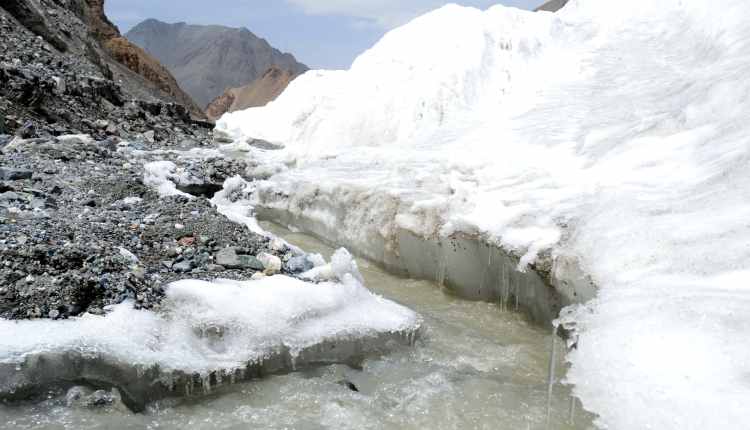
New York: If the world reaches 1.5 degrees Celsius of warming, 50 per cent of the glaciers would disappear and contribute 9 cm to sea level rise by 2100, finds an alarming study.
The study, published in the journal Science, projects that the world’s glaciers could lose as much as 40 per cent of their mass by 2100.
Researchers from Carnegie Mellon University in Pittsburgh, US, modelled glaciers around the world — not counting the Greenland and Antarctic ice sheets — to predict how they will be affected by global temperature increases of 1.5 to 4 degrees Celsius (2.7 to 5 degrees Fahrenheit) above pre-industrial levels.
The study found that with 1.5 degrees Celsius of warming, half the world’s glaciers would disappear and contribute 3.5 inches to sea level rise by 2100.
If the world reaches 2.7 degrees of warming — the estimated temperature increase based on climate pledges made at the Conference of Parties (COP26) of the UN Framework Convention for Climate Change — nearly all glaciers in Central Europe, western Canada, and the US (including Alaska) will have melted.
If warming reaches 4 degrees Celsius, 80 per cent of the world’s glaciers will disappear and contribute 15 centimetres of sea level rise.
“Regardless of temperature increase, the glaciers are going to experience a lot of loss. That’s inevitable,” said David Rounce, assistant professor at Carnegie.
The study by Rounce and team marks the first modelling study that uses satellite-derived mass change data describing all the world’s 215,000 glaciers.
The team’s sophisticated model used “new satellite derived datasets that were not available on a global level before”, said Regine Hock, a glaciology professor at the University of Alaska and the University of Oslo.
It included data from Japan’s Advanced Spaceborne Thermal Emission and Reflection Radiometer (ASTER) on NASA’s Terra satellite, as well as the USGS-NASA Landsat 8 and ESA’s Sentinel satellites.
The model accounted for glacial debris cover, which includes rocks, sediment, soot, dust and volcanic ash found on the glacier surface.
Glacial debris is typically difficult to measure due to its varying thickness, but it plays an important role because it can influence glacial melting: a thin layer of debris can enhance melting, while a thick layer can insulate and reduce it.
Glaciers in remote regions — far from human activities — are particularly powerful indicators of climate change.
Rapidly melting glaciers impact freshwater availability, landscapes, tourism, ecosystems, the frequency and severity of hazards, and sea level rise.
“Sea level rise is not just a problem for a few specific locations,” said Ben Hamlington, leader of NASA’s Sea Level Change Team.
“It’s increasing almost everywhere on Earth.”
“We are not trying to frame this as a negative look at the loss of these glaciers, but instead how we have the ability to make a difference,” Rounce said.
“I think it’s a very important message — a message of hope.”
(IANS)