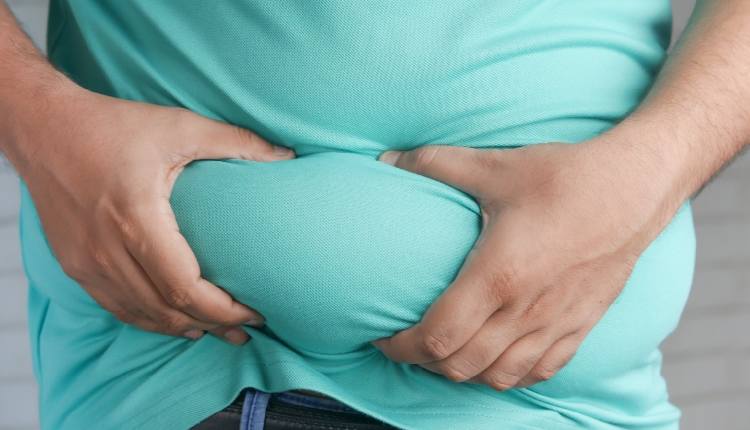
Jerusalem: A new international study has for the first time identified unique subpopulations of fat cells.
Researchers from Israel’s Ben Gurion University (BGU) noted that the study could pave the way for personalised medicine in obesity, Xinhua news agency reported.
The study, part of the international Human Cell Atlas project, mapped fat cell populations in various human fat tissues, focusing on subcutaneous and visceral fat.
Using technologies mapping RNA molecules, the team attached unique “barcodes” to RNA from individual cells, allowing them to identify distinct cell types within fat tissue.
The research, published in the journal Nature Genetics, revealed the previously uncharacterized subtypes, including fat cells involved in regulating inflammation, blood vessel formation, extracellular protein deposition, and fibrosis. In addition, one of the unique types of fat cells, identified for the first time in this research, appeared only in the intra-abdominal tissue.
Over the past 30 years, the understanding of fat tissue has evolved from merely an energy storage site to recognised for producing proteins that regulate appetite, eating, and energy expenditure, such as leptin, which influences brain control centers.
While most fat cells in subcutaneous and visceral fat were similar, subtle differences were found in their intercellular communication. Visceral fat cells were more engaged in pro-inflammatory processes, interacting with immune cells, whereas subcutaneous fat cells focused on anti-inflammatory processes.
The team also discovered that the prevalence of these unique fat cells was related to the metabolic complications of obesity, with their relative proportion in the tissue higher the more severe the insulin resistance.
According to the researchers, if unique fat cells predict personal risk for obesity complications or treatment response, the findings could significantly advance personalised obesity treatments.
(IANS)