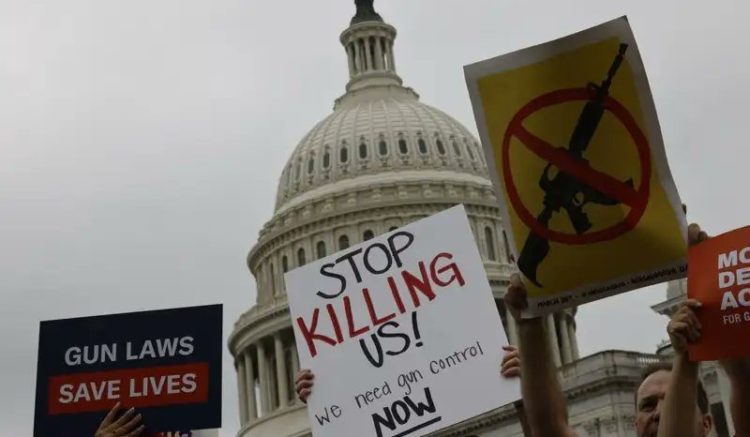
New York: In a stunning reversal of fortunes for the Democrats in the New York state assembly and President Joe Biden himself, the Supreme Court struck down the century-old NY legislation on gun laws stating that the states licensing regimes violate the constitution (an apparent reference to the 2nd amendment of 1791 that allows citizens to possess firearms and carry them outside their homes for safety).
The Supreme Court on Thursday struck down by a 6-3 majority vote a New York gun law enacted more than a century ago that places restrictions on carrying a concealed handgun outside the home — an opinion marking the widest expansion of gun rights in a decade.
“Because the State of New York issues public-carry licences only when an applicant demonstrates a special need for self-defence, we conclude that the State’s licensing regime violates the Constitution,” Justice Clarence Thomas wrote for the court’s 6-3 majority ruling, CNN reported.
The immediate fall out of the court’s ruling is that the opinion changes the framework that lower courts will use going forward as they analyse other gun restrictions, which could include the proposals currently before the Congress if they eventually become law.
The ruling could also swing voters in the margins on the bipartisan gun law set for passage in the Congress before the two-week recess. The uncertainty would be most unnerving for the 20 Senators that have worked hard on the framework legislation agreed upon and Democrats and American citizens looking for something on the table in the aftermath of the Buffalo and Texas shootings that claimed innocent lives, for meaningless violence to stop.
The Senate will take critical vote to advance the bipartisan gun bill towards final passage.
“The majority’s expansion of what the 2nd Amendment protects will have monumental ramifications far beyond carrying firearms in public — on everything from age restrictions to assault weapon bans to limits on high-capacity magazines,” says Steve Vladeck, CNN Supreme Court analyst and professor at the University of Texas School of Law.
“We’re in for a whole new slew of litigation challenging any and every gun-control measure in light of the analysis in today’s ruling,” Vladeck said.
Critics say the ruling will impair sensible solutions they think can curb gun violence.
Only about a half-dozen states have similar laws to New York’s — California, Hawaii, Maryland, Massachusetts and New Jersey — with similar regulations, but those states comprise some of the most densely-populated cities in the country.
Twenty-five states generally allow people to carry concealed weapons in most public spaces without any permit, background check or safety training, according to the Giffords Law Center to Prevent Gun Violence.
In his opinion, Thomas said that going forward the government “may not simply posit that the regulation promotes an important interest”, instead he said the judges must look to text and history when deciding whether a law passes muster.
“Only if a firearm regulation is consistent with this Nation’s historical tradition may a court conclude that the individual’s conduct falls outside the Second Amendment’s unqualified command,” Thomas said.
Dissents cite recent mass shootings
In a dissent joined by the other liberals, Justice Stephen Breyer noted the spate of gun violence and said that the court, listing several recent shootings, including the massacre at the Buffalo grocery store earlier this year. Thursday’s ruling “severely burdens States’ efforts” to curb gun violence, Breyer wrote.
“The primary difference between the court’s view and mine is that I believe the Amendment allows States to take account of the serious problems posed by gun violence that I have just described,” Breyer wrote.
“I fear that the Court’s interpretation ignores these significant dangers and leaves States without the ability to address them.”
Justice Samuel Alito, in a concurring opinion, pushed back: “And how does the dissent account for the fact that one of the mass shootings near the top of its list took place in Buffalo? The New York law at issue in this case obviously did not stop that perpetrator.”
Why the Supreme Court news site SCOTUS blog says it has a ‘public service’ role
The conservative justices also dismissed concerns defenders of New York’s gun law raised about how the law restricted the carrying of firearms into sensitive places.
“It is true that people sometimes congregate in ‘sensitive places,’ and it is likewise true that law enforcement professionals are usually presumptively available in those locations. But expanding the category of ‘sensitive places’ simply to all places of public congregation that are not isolated from law enforcement defines the category of ‘sensitive places’ far too broadly,” Thomas wrote.
First major ruling on guns in a decade
Since handing down two major Second Amendment cases in 2008 and 2010, the court has largely dodged the issue but agreed to take up the dispute after Justice Amy Coney Barrett arrived, highlighting her impact on the new conservative court, CNN analysts said.
In 2008’s District of Columbia vs Heller case, the court had held for the first time that the Second Amendment protects an individual’s right to keep and bear arms at home for self-defense. Except for a follow-up decision two years later, the justices largely stayed away from the issue infuriating gun rights advocates and even some of the justices themselves.?
Thomas and other conservatives have made clear they believe lower courts have been thumbing their noses at the Heller decision by upholding restrictions. “The Second Amendment is a disfavored right in this court,” Thomas had previously said.
The case, New York State Rifle & Pistol Association vs Bruen, concerned a New York law governing licences to carry concealed handguns in public for self-defense. It required a resident to obtain a license to carry a concealed pistol or revolver and demonstrate that “proper cause” exists for the permit. Residents must show that they have a great need for the license and that they face a “special or unique danger to their life.”
The law requires applicants who want to carry a handgun in public without restriction to show an “actual and articulable” self-defence need, as opposed to one that is “speculative or specious”.
A panel of judges on the 2nd US Circuit Court of Appeals held that New York’s law did not violate the Second Amendment. The Biden administration supported New York and told the Supreme Court in a brief that while the Second Amendment protects an individual’s right to keep and bear arms, the right is “not absolute”.
Acting Solicitor General Brian Fletcher told the justices that the law was “firmly grounded” in the nation’s history.
The petitioners in the case were Robert Nash, Brandon Koch and the New York State Rifle & Pistol Association — an NRA affiliate. They were represented by Paul Clement, a George W. Bush-era solicitor general who argued that the Second Amendment ensures a right not just to “keep arms”, but to bear them.
Nash and Koch had passed the required background checks and obtained licenses to carry guns for hunting and target practice, but they had not been able to establish a special need for self-defense that is required under the law to receive an unrestricted license.
Clement argued that the law makes it almost impossible for an ordinary individual to obtain a license because the “proper cause” standard is so demanding and left to the “broad discretion” of the licensing officer.
“Good, even impeccable, moral character plus a simple desire to exercise a fundamental right is not sufficient. Nor is living or being employed in a high crime area,” Clement said.
Nash, for instance, requested to carry a handgun for self-defense after a string of robberies in his neighborhood. But he was denied because he did not demonstrate a special need for self-defense. Koch wanted a similar licence, and he was able to cite his experience of participating in safety training courses. He too was denied.
(IANS)